

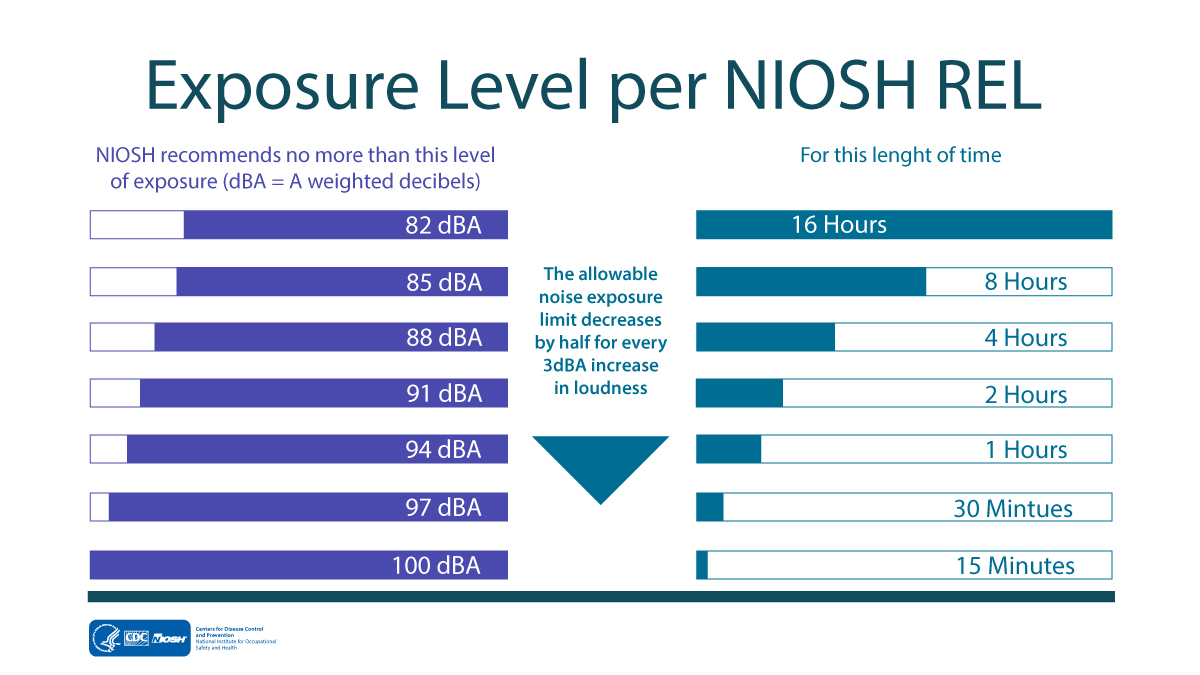
The NIOSH recommended exposure limit (REL) for occupational noise exposure is 85 A-weighted decibels (dBA) over an eight-hour shift.
If workers are repeatedly exposed to noise at or above the REL, employers must provide a hearing loss prevention program.
Noise levels are likely hazardous if a person must raise their voice to speak with someone is an arm's length away.
Hearing loss from routine noise exposure is 100% preventable and is best addressed by creating a quieter workplace.
Decibels (dB) are a scale for measuring noise. A-weighted noise levels or dBA is used to predict hearing risk. Noise above 85 dBA is considered hazardous.
To properly control and reduce noise in the workplace, you should know:
Occupational noise measurements are usually reported in the following ways:
A noise dose of 100% or more means that a worker has exceeded their daily limit for noise exposure.
The two basic instruments for characterizing noise are sound level meters (SLMs) and dosimeters.
You can use SLMs to:
When noise levels in an area are fairly constant, you can use SLMs to estimate the noise exposure in an area.
Use personal noise dosimeters to best assess a worker's personal noise exposure. Dosimeters average noise levels over time and calculate a noise dose.
Time Weighted Average (TWA) is the average noise level during a shift (usually 8 hours). It considers both noise levels and how long the employee is exposed at each noise level.
Measure workplace areas with a sound level meter (SLM) and create a noise map of facility areas. If an SLM is not available, sound measurement apps can provide a measure of area noise but may not comply with regulatory requirements. You can download the NIOSH SLM app on iOS devices.
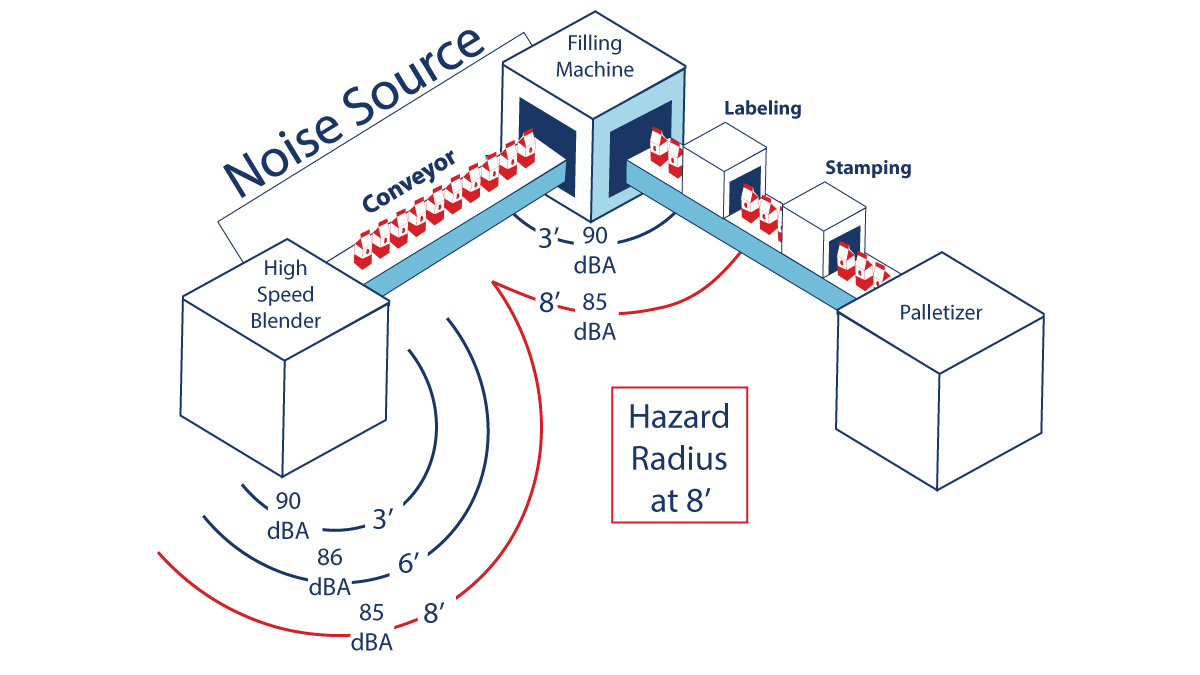
After completing a noise map, identify the loudest areas on the map and the equipment in those areas. This can help determine which equipment to replace or where to implement noise controls.
If you can't determine the noise levels safely or accurately, consult the equipment vendor or a noise control engineer.
Measure individual worker noise exposures using a personal dosimeter in areas with high noise. Dosimeters calculate a worker's noise dose.
Enroll workers whose noise dose exceeds 100% of the NIOSH REL in a hearing loss prevention program.
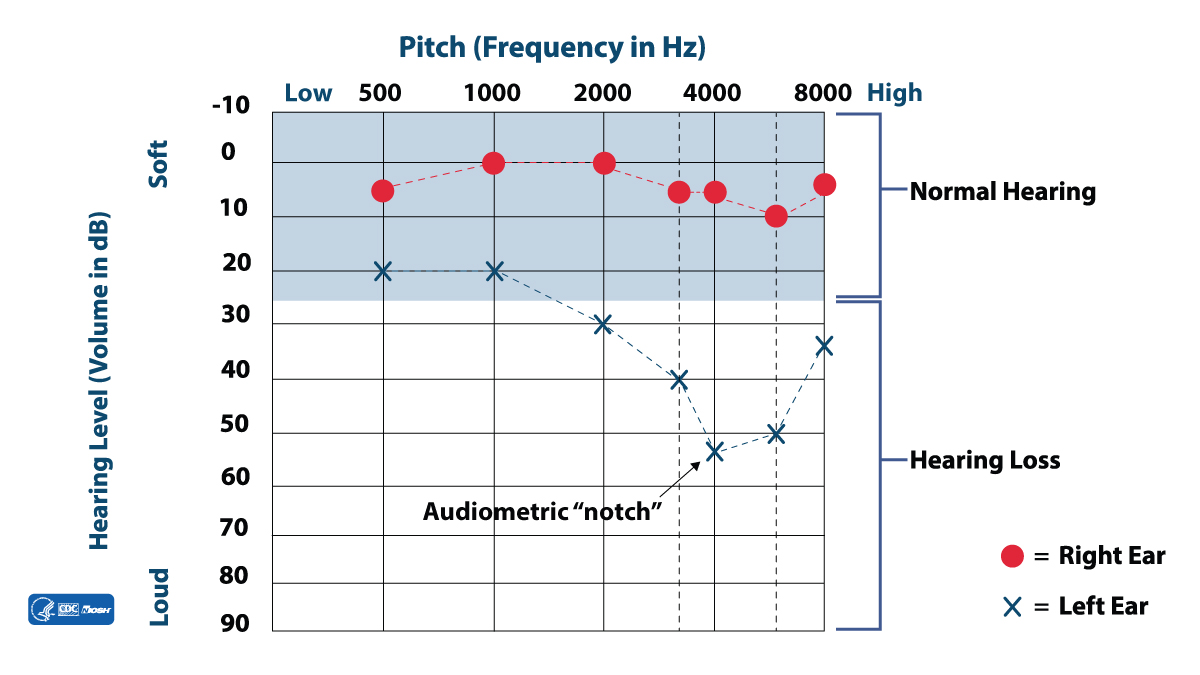
Audiometry is a hearing test that measures the lowest level of sound a person can hear (called thresholds) across a range of frequencies (pitches).
An audiogram is a graph of hearing thresholds at various frequencies in each ear. Thresholds which are 25 dB HL (hearing level) or better (lower) are considered normal for adults. Noise exposure initially affects hearing most at frequencies around 3000-6000 Hz, creating a "notch" in the audiogram.
NIOSH recommends annual audiometric testing for workers exposed to noise above the REL. Testing should be performed by a professional certified by the Council for Accreditation in Occupational Hearing Conservation (CAOHC) or equivalent certification.
Conduct testing on workers when they are first enrolled in a hearing loss prevention program. This is called baseline testing. Baseline testing provides a record of workers' hearing from the beginning and helps determine if there is any change to workers' hearing over time.
NIOSH recommends that employers obtain baseline tests within 30 days of initial exposure for newly exposed workers. Workers should be away from hazardous noise exposure for at least 12 hours before baseline testing is done.
Unlike baseline testing, annual hearing tests should be done as close to the end of a worker's shift as possible (no preceding quiet period). This helps catch temporary changes in hearing before the changes become permanent.
Results of annual hearing tests should be compared to results from the baseline hearing test to check for significant threshold shift (STS). NIOSH considers a 15 dB change in hearing threshold at any frequency to represent an STS. If an STS is noted during an annual hearing test, the worker should be retested within 30 days to confirm. Like the baseline audiogram, workers should have at least a 12-hour quiet period before a confirmation test so that the tester can tell whether the shift was temporary or permanent.
Workers who develop an STS – whether temporary or permanent – should be notified. Steps should be taken to prevent further change in hearing. These steps could include refitting with hearing protection, additional training on noise exposure, or re-assignment to a quieter area.
You can find more detailed information on audiometric monitoring in the NIOSH Practical Guide for Preventing Occupational Hearing Loss.
Frequency refers to how low or high the "pitch" of the sound is. Frequency is measured in Hertz (Hz).
You should tell workers they are having their noise exposure monitored and provide them with an explanation of the results. When workers know their daily noise exposure and the workplace noise level, they can help make a hearing loss prevention program effective.
Involve workers in the noise monitoring process. They can provide important information about the work environment, machinery operation, and specific job tasks. Encourage workers to tell you when changes in equipment or production occur. Noise levels should be re-measured whenever a change is made that could affect exposure levels.